(ENGLISH BELOW)
 IL SOTTOSUOLO
IL SOTTOSUOLO
E' facile pensare che il sottosuolo di Piazza Colosseo sia omogeneo, proprio perchè il suolo si presenta come un verde prato o una piatta strada, senza dune o irregolarità molto visibili. Ma non è così.
Quest'area è " divisa " a metà da due tipi di sottosuoli diversi: uno è un conglomerati e sabbie vulcaniche (quindi molto solido), l'altro invece è costituito da sedimenti alluvionali (provenienti dal Fosso Labicano).
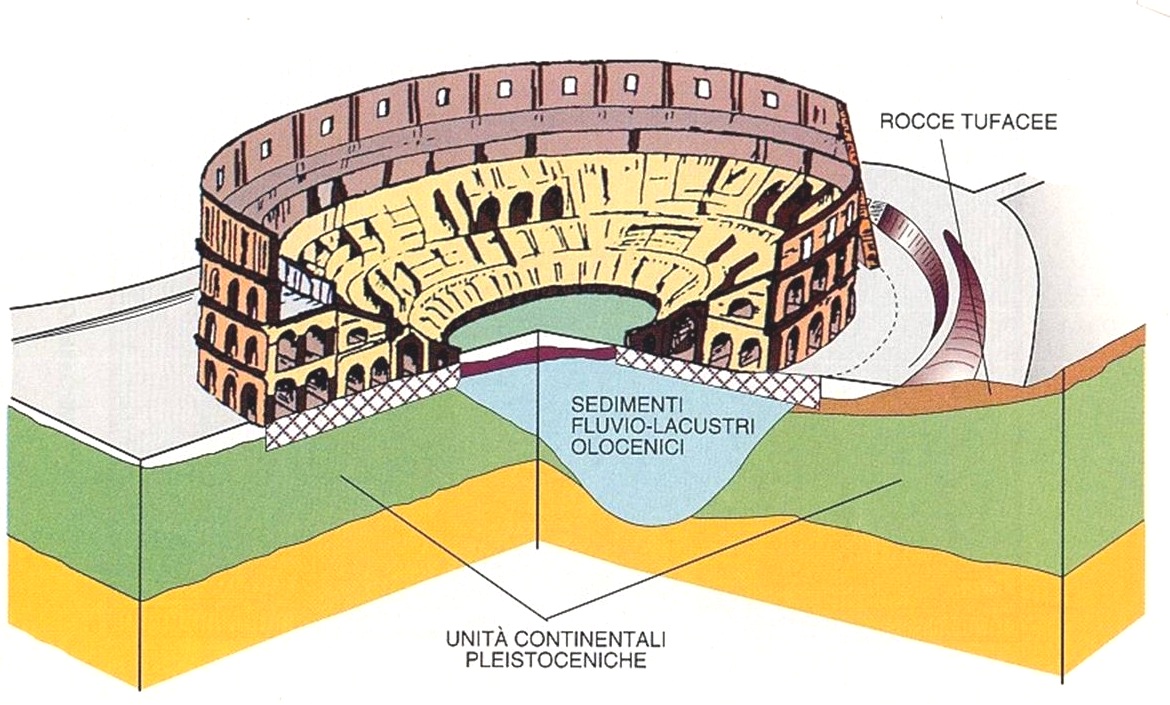
(i diversi tipi di terreno della piazza)
Un sottosuolo in parte molto solido e in parte debole, di per se non da grossi problemi a quest'area. I veri problemi si presentano alla presenza di onde sismiche, quindi alle scosse di terremoto.
LA RISONANZA SISMICA
Le onde sismiche si comportano in modo diverso a seconda del terreno che incontrano, mi spiego meglio. Quando delle onde incontrano un terreno roccioso o un terreno solido, le onde vengono assorbite dal terreno, venendo quindi attenuate, Se invece le onde incontrano un terreno irregolare e poco consolidato, esse verranno amplificate. Questo fenomeno (naturale) viene chiamato risonanza.
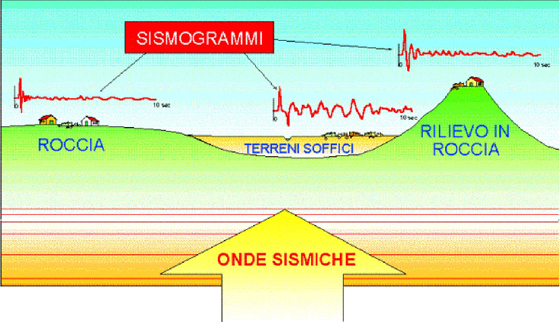
(la risonanza nei diversi terreni)
LE CONSEGUENZA A ROMA
Anche se Roma non è una zona particolarmente sismica, ci sono comunque stati dei terremoti particolarmente devastanti, come quelli del 443 e 484 d.C., quello del 1349 e quello del 1915 ma, alla presenza di questo tipo di sottosuolo molto poco consolidato, anche i terremoti minori acquistano la loro importanza.
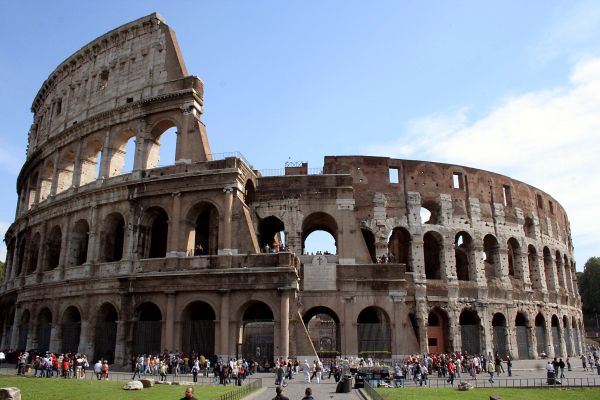
Una dimostrazione "pratica" degli effetti della risonanza la possiamo avere osservano il Colosseo.
Il Colosseo, infatti, è stato costruito per metà sulla parte solida, e per metà sulla parte meno consolidata. Proprio per questo, una metà dell’anfiteatro Flavio si presenta molto più danneggiata dell'altra, che conserva ancora i tre ordini di archi fino alla sommità. L’anello più esterno dell’antico Anfiteatro Flavio (l’antico nome del Colosseo), risulta interamente distrutto.
Come puoi vedere da questa foto, ad un certo punto l'anello esterno si interrompe, segno che da li in poi il sottosuolo è più fragile.

COME LOGGARE LA CACHE
Per poter loggare la cache dovrete rispondere alle seguenti domande e mandarmi le risposte per messaggio privato al mio profilo. Potete loggare la cache prima di ricevere la conferma della correttezza delle risposte, in caso dovessero esserci errori, vi contatterò.
Le coordinate della cache indicano il centro del Colosseo, essa è solo una posizione fittizia, sarà necessario visitare solo i 2 waypoint (Nord e Sud) nell'ordine che preferite.
- Cos'è la risonanza?
- Recati al waypoint Sud e a Nord, uno si trova sul terreno molto solido e l'altro sul terreno fragile. Osserva bene il terreno e annota, secondo te, in quale dei due ti trovi, elencandone i motivi e le riflessioni che hai fatto per arrivare a quella conclusione. (in caso di dubbi, vedi suggerimento)
- Riprendendo la domanda 2, ne consegue che la zona del Colosseo che poggia sulle rocce vulcaniche è la parte.... (Nord/Sud). Mentre la parte.... (Nord/Sud) poggia su sedimenti alluvionali.
- (facoltativo) Mi piacerebbe molto se scattassi una foto con te (e il gps) da qualche parte nel GZ.
ENGLISH
THE UNDERGROUND
It 's easy to think that the subsoil of Piazza Coliseum is homogeneous, just because the land looks like a green lawn or a flat road, no dunes or irregularities very visible. But is not so.
This area is "divided" in half by two types of subsoils different: one is a conglomerate and volcanic sands (very solid), the other is made up of alluvial sediments (from Fosso Labicano).

(Different types of soil of the square)
A subsoil in part very solid and partly weak, per se not to big problems in this area. The real problems arise in the presence of seismic waves, and the earthquakes.
SEISMIC RESONANCE
Seismic waves behave differently depending on the terrain encountered, I'll explain. When the waves encounter a rocky terrain or solid ground, the waves are absorbed by the ground, then being attenuated, If the waves encounter an uneven ground and weakly bonded, they will be amplified. This phenomenon (natural) is called resonance.

(Resonance in different soils)
THE RESULT IN ROME
Although Rome is not a particularly seismic, there were however of earthquakes particularly devastating, such as those of 443 and 484 AD, the one of 1349 and one of 1915 but, in the presence of this type of subsurface very little consolidated, even earthquakes children acquire their importance.
A demonstration "practice" of the effects of the resonance we have observed the Coliseum.
The Colosseum, in fact, was built on the solid half and half on the less well-established. For this reason, one half of the Flavian Amphitheatre presents much more damaged than the other, which still has three rows of arches to the top. The outer ring of the ancient Flavian Amphitheatre (the ancient name of the Colosseum), was entirely destroyed.
As you can see from this picture, at some point the outer ring is interrupted, a sign that from then on the ground is more fragile.

Logging HOW THE CACHE
To be able to log the cache you will have to answer the following questions and send the answers to private message to my profile. You can logging cache before receiving confirmation of the correctness of the answers, if there were mistakes, I will contact you.
Cache coordinates indicate the center of the Colosseum, it is only a fictitious position, you will need to visit only 2 waypoint (North and South) in any order.
- What is resonance?
- Went to the waypoint south and north, one is on very solid ground and the other on fragile ground. Look carefully at the ground and note, in your opinion, which of the two you are, listing the reasons and reflections that you did to get to that conclusion. (If in doubt, see Tip)
- Taking up the second question, it follows that the area of the Colosseum that rests on volcanic rocks is the part .... (North / South). While the .... (North / South) rests on alluvial sediments.
- (Optional) I would like if you take a picture with you (and GPS) somewhere in the GZ.
