Red River Floodway EarthCache
-
Difficulty:
-

-
Terrain:
-
Size:  (not chosen)
(not chosen)
Please note Use of geocaching.com services is subject to the terms and conditions
in our disclaimer.
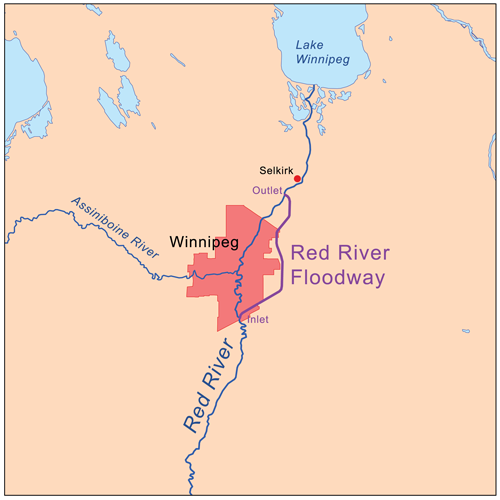
The Red River Floodway is an artificial flood control waterway first used in 1969. It is a 47 km long channel which, during flood periods, takes part of the Red River's flow around the city of Winnipeg to the East and discharges it back into the Red River below the dam at Lockport.
The Red River flows across the flat lakebed of the ancient glacial Lake Agassiz, an enormous glacial lake created at the end of the Wisconsin glaciation from meltwaters of the Laurentide ice sheet. As this continental glacier decayed, its meltwaters formed the lake, and over thousands of years sediments precipitated to the bottom of the lakebed. These lacustrine soils are the parent soils of today's Red River Valley.
The river itself is very young; it began only after Lake Agassiz drained, about 9,500 years ago. The word "valley" is a misnomer. While the Red River drains the region, it did not create a valley wider than a few hundred feet, and the much-wider floodplain is the lakebed of the glacial lake. It is remarkably flat; from its origin near Breckenridge, Minnesota to the international border near Emerson, Manitoba, its gradient is only about 1:5000 (1 metre per 5 kilometres), or approximately 1 foot per mile.
The river, slow and small in most seasons, does not have the energy to cut a gorge. Instead it meanders across the silty bottomlands in its progress north. In consequence, high water has nowhere to go, except to spread across the old lakebed in "overland flooding". Heavy snows or rains, on saturated or frozen soil, have caused a number of catastophic floods, which often are made worse by the fact that snowmelt starts in the warmer south, and waters flowing Northward are often dammed or slowed by ice.
One of the most significant flood protection measures in Manitoba is the Red River Floodway, which protects the City of Winnipeg.
The original floodway was built between 1962 and 1968 and cost $63 million. At the time, excavation of the floodway channel was the second largest earth moving project in the world (second only to the Panama Canal and larger than the Suez Canal project). Since 1968, it has prevented more than $40 billion in flood damage in Winnipeg. It is often referred to as Duff's Ditch in recognition of then-Premier Duff Roblin, who spearheaded the development of the floodway.
Used many times over a period of nearly 30 years, it prevented flooding in the city. In 1997, Manitoba experienced a major flood, which forced the evacuations of communities in the Red River Valley and came close to reaching the floodway's capacity and threatening the protection of Winnipeg. It was determined that the floodway needed to be expanded to ensure future safety, and so construction began in 2003.

Parking coordinates have been given. From there, you may walk or cycle for approximately 1.25km along the Duff Roblin Parkway Trail, which parallels the floodway itself. You will learn about measures that took place to ensure the future safety of the Red River Floodway.
To Log a find on the earthcache, you must answer 5 questions. Send the answers via the link to the cache owner. Once answers have been approved, you may log online.
1. What efforts have been taken to reduce erosion on the banks of the floodway?
2. At Waypoint 2, look around you - even through snow, you should be able to see evidence of a particular prairie grass which is making a comeback here. Which grass do you think it is?
3. What is now banned along the floodway, and why?
4. How was groundwater protected during the floodway expansion project?
5. There is an object 29m to the North of the final waypoint - what is it?
OPTION: Take a picture of you and/or your GPSr at the final location with the floodway in the background.


We have earned GSA's highest Earthcache Masters level for finding at least 20 Earthcache Discoveries, Discovering an Earthcache in at least 5 States/Countries and for placing 3 Earthcaches for others to Discover:
|
 |
Additional Hints
(No hints available.)